Eyes, JAPAN
Neural Radiance Fields
zeke
Neural Radiance Fields
Introduction: Novel view synthesis
Novel view synthesis is the complicated and difficult task of generating images of an object or a scene from viewpoints that were not present in the original dataset of images. Some of the applications include but are not limited to: VR, AR, Video games, medical imaging, architectural visualization etc. Researchers have been using the exponential growth of AI and deep learning structures to develop new fascinating tools to combat this issue. Neural Radiance Fields, one of the many methods available, has gained a lot of attention in the past few years and seems extremely promising, solving a lot of difficult issues that come with novel view synthesis. This blog will explain the science behind Neural Radiance fields, its benefits and some starting points if you are interested in creating your own 3D models.
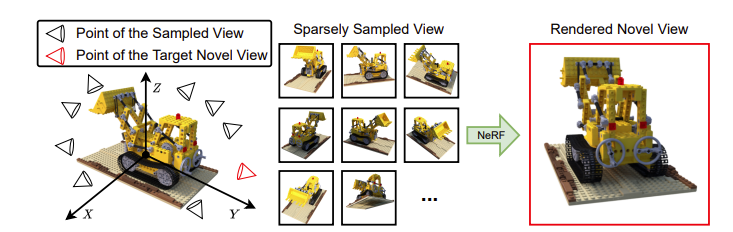
What is a Neural Radiance Field or NeRF?
A Neural Radiance Field is an implicit continuous function that represents a 3D scene. Although this sounds complicated, the basic idea of NeRF is quite simple. Essentially, a 8-layer multi-layer perceptron (MLP) is given the input of : a point in the space of the scene (x,y,z) and it’s the cameras viewing direction ( θ, φ), and it will be trained so that it can predict the color and the density of that certain point in the scene. In layman’s terms, the model learns how to predict what you would see if you were looking at the scene from a certain viewpoint. Hence its great success in creating completely novel views from anywhere in the scene.
How does it fare against other methods? What makes it special?
There are a few notable points it has over other methods and they all contribute to the extremely high quality of NeRFs. Firstly, since the function modeled is continuous, it means it can output an image of the scene from any angle. Secondly, it only needs several input images that can be taken from anywhere to produce a high quality output. Other methods require a more meticulous and calculated arrangement of photos to produce an output of the same quality. Thirdly, NeRF’s ability to render transparent, translucent and reflective surfaces is clearly superior, with previous models and techniques having struggled on the problem for many years. All these factors combine to make NeRF such a promising idea.
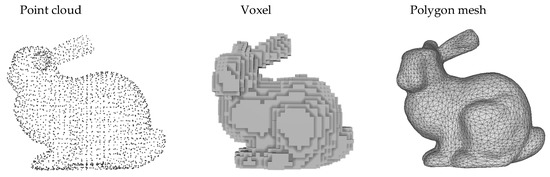
Point cloud, voxel, polygon mesh which are explicit representations of a scene
Applications and current research
There has been a lot of optimization and modification of the original NeRF model, leading to significantly faster training times with less storage cost, with some models being able to be trained in less than 10 minutes! Moreover, it’s being combined with diffusion models, leading to editing entire scenes with just a text prompt. It seems as if the possibilities are endless as any advancement and novel idea that can be applied to a 2D image, can most likely be applied to a NeRF scene as well.
Some of the few cool applications include:
- Combining Nerf with text-to-image models: Instruct-Nerf2Nerf https://github.com/ayaanzhaque/instruct-nerf2nerf
- Nerf for outdoor screnes: Nerf in the Wild https://nerf-w.github.io/
- Editing Nerf with text prompts: CLIP-Nerf https://cassiepython.github.io/clipnerf/
- Rendering videos of humans: Human-Nerf https://grail.cs.washington.edu/projects/humannerf/
- Real-time rendering of Nerf for VR/AR: RT-Nerf https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.01120
- Original Nerf paper: https://www.matthewtancik.com/nerf
How to get started in NeRF
Even if you don’t completely understand it, you can still try and model things yourself! There is plenty of documentation, videos and content on how to create your very first NeRF model. My recommendation is using NerfStudio as it is the most user-friendly tool currently out there. there is a Github and plenty of tutorials on Youtube to get you started. The only difficult part may be converting your custom input data, image or video, into readable data for the model; however, Nerf Studios documentation has detailed instructions on how to do this. Although there are quite a lot of dependencies you will need to install and it does require a reasonable amount of hardware resources so keep this in mind! Try out this new emerging technique yourself! Nvidia
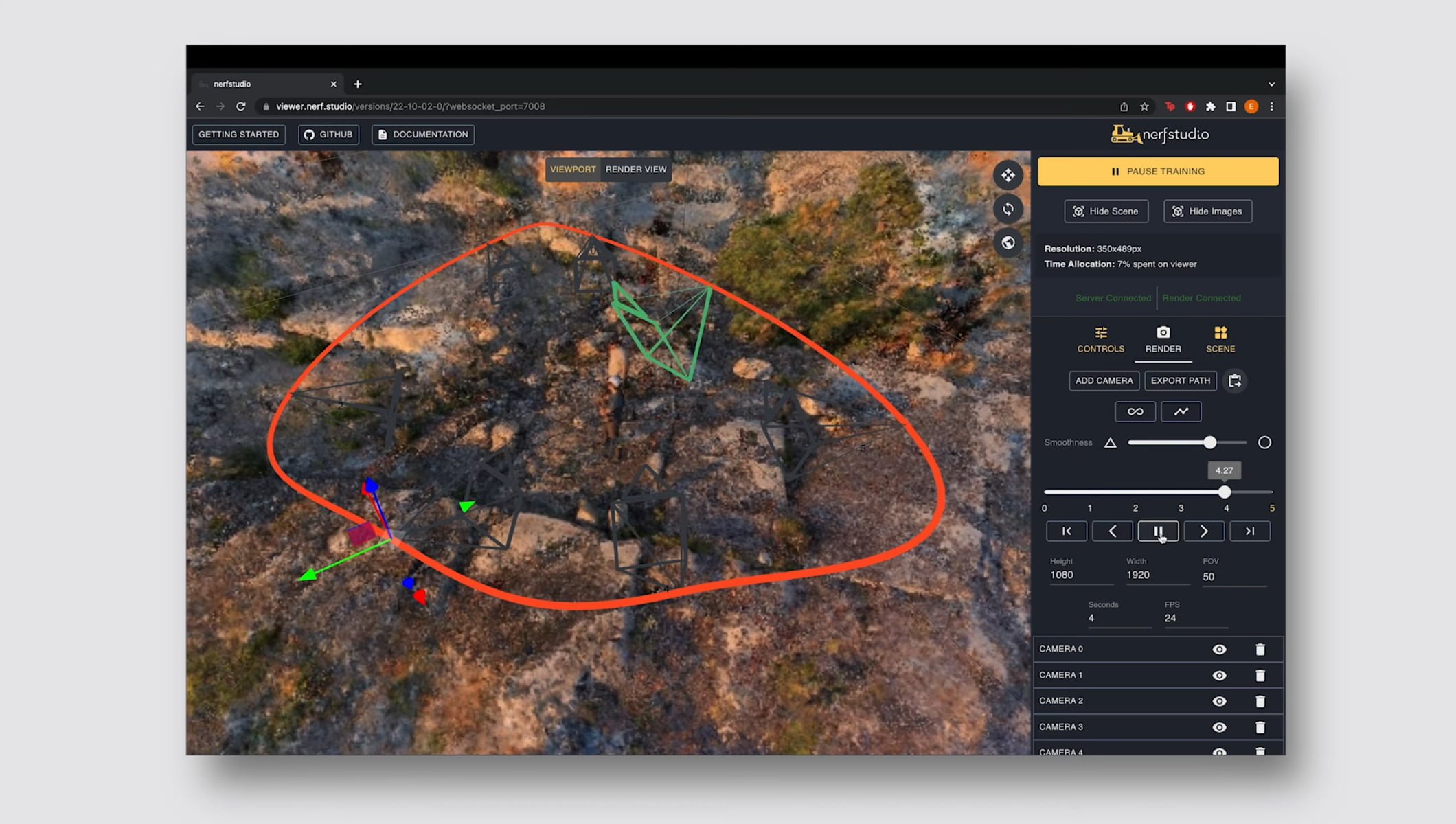
Photo taken from Nerfstudio GUI application
Conclusion
Nerf is an emerging and extremely interesting technique with hundreds of papers being released on the topic in the past 3 years. As seen from some of the examples in this blog, there have been diverse and creative applications of the Nerf, showcasing the potential the technique has with some high quality outputs using only a sparse set of input images and trained in a relatively short period of time. A few Github repositories like NerfStudio has made using Nerf a lot more available to the public by creating a simple and easy to use GUI way to handle the training and rendering of NeRF outputs. With more papers and new Nerf models being released monthly, its only a matter of time until the technique has been optimized to the point where it will be accessible to everyone and in the near future you might only need your phone to create wonderful 3D scenes.
 2026/02/27
2026/02/27 2026/01/23
2026/01/23 2025/12/12
2025/12/12 2025/12/07
2025/12/07 2025/11/06
2025/11/06 2025/10/31
2025/10/31 2025/10/24
2025/10/24 2025/10/03
2025/10/03